Custom Zinc Die Casting Services
- Zinc die casting process has the advantages of high production efficiency, good surface quality, dimensional accuracy, high material utilization rate, etc.
- It is widely used in the manufacture of parts in the fields of automobiles, electronics, home appliances, mechanical equipment, etc.
- Excellent Dimensional Stability
- Multiple Materials Available
- Easy Finishing
- Low Energy Costs
- Long Tool Life
Zinc Die Casting Methods
Zinc die casting methods, including vacuum, hot chamber, cold chamber, high-pressure, gravity, and squeeze casting, each offer unique advantages for precision, efficiency, and part quality.

Zinc Vacuum Die Casting
Reduces air entrapment, enhancing part quality. Molten zinc is injected into a vacuum-sealed die, minimizing porosity and improving mechanical properties. Achieves high dimensional accuracy, typically within ±0.02 mm, and provides a superior surface finish.

Zinc Hot Chamber Die Casting
Involves injecting molten zinc directly from a furnace into the die. Highly efficient, with short cycle times and precision, producing parts with tolerances within ±0.05 mm. Results in excellent surface quality, ideal for high-volume production.

Zinc Cold Chamber Die Casting
Used for higher melting point zinc alloys. Molten zinc is ladled into the injection chamber, then forced into the die. Yields precise parts with tolerances within ±0.1 mm and good mechanical properties, suitable for medium to high-volume production.

Zinc High-Pressure Die Casting
Involves applying intense pressure while pumping molten zinc into a die. Ensures excellent dimensional accuracy, typically within ±0.02 mm, and surface finish. Ideal for creating intricate, thin-walled parts with excellent uniformity and production efficiency.
Zinc Gravity Die Casting
Uses gravity to fill the die with molten zinc. Ideal for simpler, less intricate parts. Offers good dimensional accuracy, generally within ±0.2 mm, and surface quality, with lower production costs compared to high-pressure methods.

Zinc Squeeze Die Casting
Integrated with die casting and forging, molten zinc undergoes pressure during solidification, minimizing porosity while enhancing mechanical properties and achieving ±0.05 mm dimensional accuracy for a high-quality finish in miniature applications.
Available Zinc Alloys Material
Zinc die casting offers versatile alloys like ZAMAK 2, 3, 5, 7, ZA 8, and ZA 27, each tailored for specific strength, conductivity, and application needs.

ZAMAK 2
- Composition: 99.99% Zn, 4% Al, 3% Cu
- Melting Point: 380°C (716°F)
- Tensile Strength: 397 MPa
- Thermal Conductivity: 113 W/m·K
- Application: High-strength parts, gears, connectors, and applications requiring wear resistance.

ZAMAK 3
- Composition: 96% Zn, 4% Al
- Melting Point: 380°C (716°F)
- Tensile Strength: 283 MPa
- Thermal Conductivity: 113 W/m·K
- Application: General-purpose parts, automotive components, household appliances, and hardware.

ZAMAK 5
- Composition: 96% Zn, 4% Al, 1% Cu
- Melting Point: 380°C (716°F)
- Tensile Strength: 334 MPa
- Thermal Conductivity: 113 W/m·K
- Application: Parts requiring higher strength than ZAMAK 3, such as automotive parts, hardware, and electronic components.
ZAMAK 7
- Composition: 99.99% Zn, 4% Al, 0.02% Mg
- Melting Point: 380°C (716°F)
- Tensile Strength: 283 MPa
- Thermal Conductivity: 113 W/m·K
- Application: Thin-walled components, intricate designs, and applications requiring improved ductility and better finish.

ZA 8
- Composition: 92% Zn, 8% Al
- Melting Point: 388°C (730°F)
- Tensile Strength: 410 MPa
- Thermal Conductivity: 115 W/m·K
- Application: Stronger and more durable parts, such as mechanical components, automotive parts, and hardware.

ZA 27
- Composition: 73% Zn, 27% Al, 2.5% Cu
- Melting Point: 382-477°C (719-891°F)
- Tensile Strength: 400 MPa
- Thermal Conductivity: 121 W/m·K
- Application: High-performance applications, including bearings, bushings, gears, and other wear-resistant components.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc die casting offers various benefits and challenges, making it suitable for many manufacturing needs. This section outlines key advantages and disadvantages to help you decide if it fits your project.
Pros
- Excellent dimensional stability.
- Cost-effective for high volumes.
- Low melting point, easy reshaping/redesign.
- Ability to create complex shapes with thin walls.
- Fast production cycles, reducing machining needs.
- Supports various surface treatments.
- Longer die service life.
Cons
- Not ideal for all lightweight applications.
- Limited to lower melting point alloys.
- Potential porosity issues.
- Requires precise temperature control.
- High initial tooling costs.
- Surface defects if not controlled.
- Limited to smaller component sizes.
Our Zinc Die Casting Projects
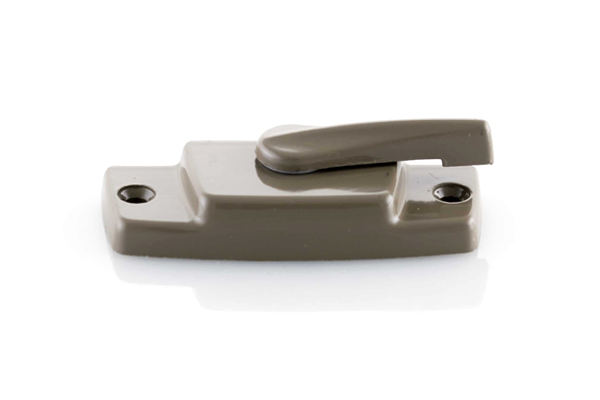
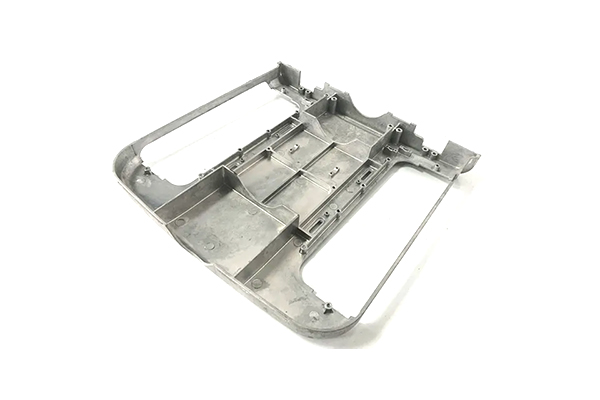
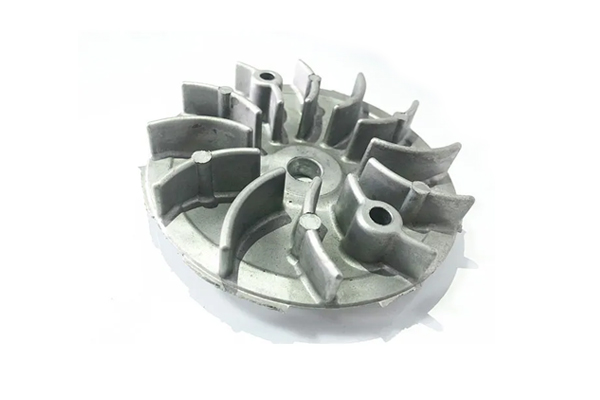
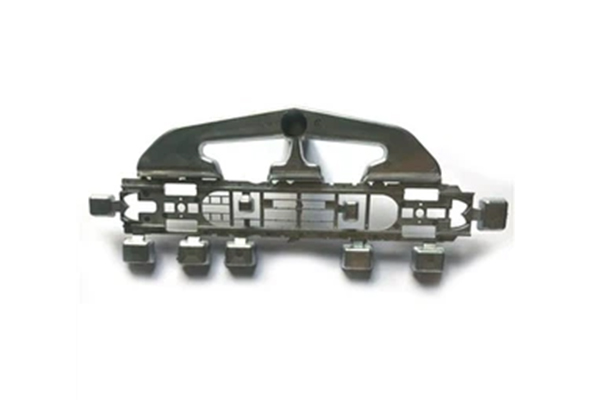




Surface Treatment
Zinc die castings can undergo eight surface treatments to enhance their properties, each offering unique benefits for corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetics.








Popular Questions
What aspects of designing for Zamak die casting should be taken into account?
Design considerations include draft angles, wall thickness uniformity, parting lines, gating and venting, and the placement of ejector pins to ensure easy removal from the mold and minimize defects.
What are the typical applications of zinc pressure die casting?
Zinc die casting is commonly used for producing automotive components, electronic housings, consumer goods, plumbing fixtures, and various industrial parts requiring high precision and durability.
What are the mechanical properties distinguishing die cast zinc and aluminum alloys?
Die cast zinc alloys are harder and more machinable, ideal for electronics. Aluminum alloys offer superior strength and impact resistance, suited for construction and transportation.
What are zinc die casting's benefits?
Zinc die casting offers high precision, excellent strength-to-weight ratio, superior surface finish, recyclability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness in high-volume production.
What industries use zinc sand casting?
Industries like art casting, ornamental products, and specialized mechanical parts benefit from zinc sand casting’s versatility and cost-effectiveness.
How does miniature zinc die casting work?
It works by injecting molten zinc alloy into precision molds to create tiny, detailed components used in electronics, medical devices, and automotive applications.
