Magnesium Die Casting Manufacturer
- Magnesium die casting offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for lightweight, durable components in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- It provides superior dimensional stability and corrosion resistance, ensuring high-quality and long-lasting products.
- Outstanding Dimensional Control
- Ultra-Thin Wall Design Options: 0.5 to 1.0 mm
- High Strength and Stiffness-to-Weight Ratio
- Long Tooling Life to Lower Total Production Cost
- Abundant Finishing Options
Magnesium Die Casting Process
Magnesium die casting is a manufacturing process where molten magnesium is injected into a mold to create precise, lightweight, and high-strength parts.
Melting
Magnesium alloys are melted at 650°C for optimal fluidity. The melting process ensures consistent alloy composition and eliminates impurities for casting integrity.
Injection Molding (Casting)
Molten magnesium is injected into molds at pressures between 1,500 and 25,000 psi, filling detailed cavities rapidly to form precise shapes.
Cooling and Solidification
The molten magnesium solidifies within 5 to 15 seconds, minimizing thermal stress and achieving high dimensional accuracy with rapid cooling rates.
Finishing and Inspection
Trimmed and machined parts undergo anodizing, painting, and powder coating. Every component is examined for flaws, structural integrity, and dimensional accuracy.
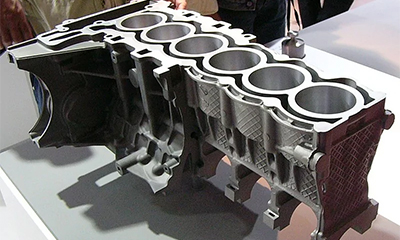
Magnesium Die Casting Methods
Magnesium die casting methods include high-pressure, low-pressure, hot chamber, cold chamber, vacuum, and squeeze casting, each suited for various part sizes and applications.
Magnesium High-Pressure Die Casting
Molten magnesium is injected into molds at 2000-4500 psi, achieving rapid cycles and precise dimensions, ideal for automotive and electronics parts with thin walls down to 1mm.

Magnesium Low-Pressure Die Casting
Uses 15-150 psi to push molten magnesium into molds, providing better fill control and mechanical properties, suitable for larger automotive and industrial parts with fewer defects.

Magnesium Hot Chamber Die Casting
Directly injects molten magnesium from a furnace at 3000-5000 psi, allowing fast cycles, ideal for small to medium components up to 10 kg.

Magnesium Cold Chamber Die Casting
Separately melted magnesium is transferred to the casting machine, offering better temperature control for larger, complex parts over 20 kg, with injection pressures of 2000-4500 psi.

Magnesium Vacuum Die Casting
Evacuates air before injecting molten magnesium, reducing porosity and enhancing properties, ideal for high-integrity aerospace components and precision-engineered parts.

Magnesium Squeeze Casting
Molten magnesium is poured into molds and compressed up to 15,000 psi, reducing porosity, and enhancing properties, suitable for high-strength parts over 30 kg with excellent surface quality.
Common Magnesium Alloy Materials
Common magnesium alloys for die casting include AZ91D, AZ91HP, AM60B, AM50, AS41, AE42, AM20, and AZ31, each offering unique properties and applications.

AZ91D
- Composition: 9% aluminum, 1% zinc, rest magnesium.
- Characteristics: Excellent castability, good mechanical properties, high corrosion resistance.
- Application: Used in automotive engine blocks, transmission cases, steering columns, and fuel tank caps.

AZ91HP
- Composition: Similar to AZ91D but with higher purity levels.
- Characteristics: Improved ductility, better corrosion resistance.
- Application: Suitable for high-strength electronic housings.

AM60B
- Composition: 6% aluminum, rest magnesium.
- Characteristics: High impact and elongation properties, good castability.
- Application: Ideal for automotive safety components like instrument panels.

AM50
- Composition: 5% aluminum, rest magnesium.
- Characteristics: Good combination of ductility and strength, better elongation and impact resistance.
- Application: Used for automotive seat frames and steering wheels.

AS41
- Composition: 4% aluminum, 1% silicon, rest magnesium.
- Characteristics: Good creep resistance, suitable for high-temperature applications.
- Application: Used in aerospace engine casings.

AE42
- Composition: 4% aluminum, 2% rare earth, rest magnesium.
- Characteristics: Excellent creep resistance, good mechanical properties at elevated temperatures.
- Application: Ideal for automotive powertrain components.

AM20
- Composition: 2% aluminum, rest magnesium.
- Characteristics: High ductility and impact resistance, lower strength compared to higher aluminum content alloys.
- Application: Suitable for automotive dashboard supports.

AZ31
- Composition: 3% aluminum, 1% zinc, rest magnesium.
- Characteristics: Good combination of strength and ductility, good formability and weldability.
- Application: Used in automotive body panels and aerospace fuselage sections.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Copper Die Casting
Discover the advantages and disadvantages of magnesium die casting to determine its suitability for your manufacturing needs.
Pros
- High strength-to-weight ratio.
- Outstanding dimensional control.
- Rapid production.
- Exceptional thin wall capability.
- Excellent dimensional stability/repeatability.
- Good finishing characteristics.
Cons
- Not as stable as aluminum castings.
- Flammability risks.
- Complex post-production processing.
- Limited structural applications.
- Required machines are expensive.
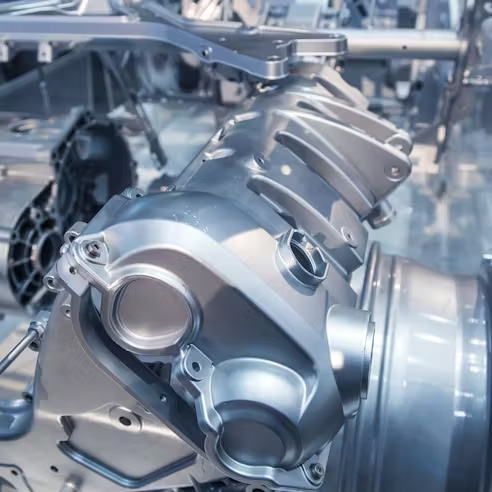
Our Magnesium Die Casting Projects
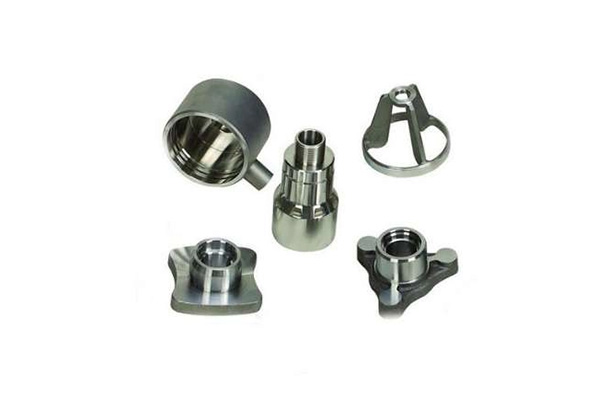
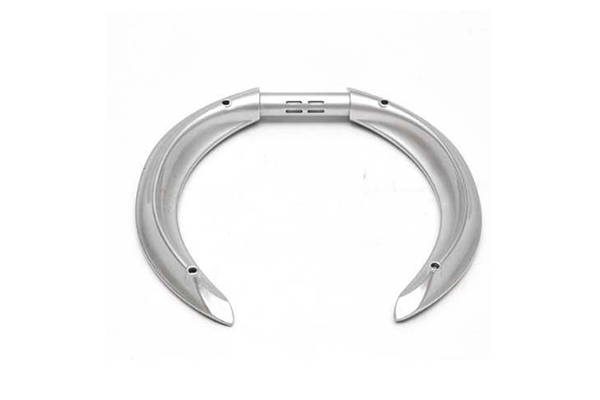
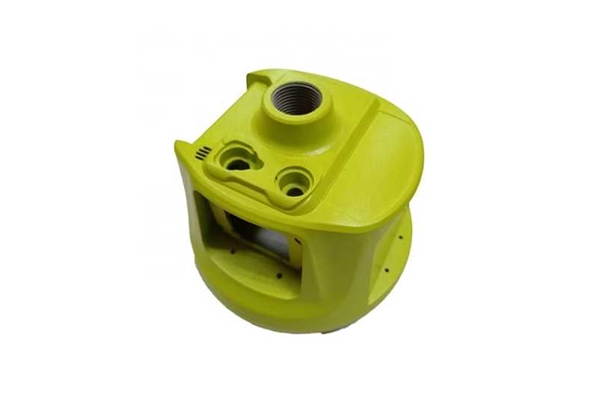






Surface Treatments Options
Surface treatment enhances magnesium die casting’s corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetics. Common methods include anodizing, plating, painting, and chemical coatings, etc.
- Chromate conversion coating
- Smoothing and polishing
- Bead blasting
- Anodizing
- Powder coating
- E-coat (Electrophoretic Coating)
- Passivation
- Phosphate coating
Popular Questions
How does magnesium aluminum alloy die casting benefit electronics?
Magnesium aluminum alloy die casting offers good electromagnetic shielding, lightweight properties, and excellent heat dissipation, making it suitable for electronic housings and components.
How does magnesium AZ91D die casting compare to aluminum die casting?
Magnesium AZ91D die casting is lighter and has better damping properties than aluminum, but aluminum generally offers better strength and thermal conductivity.
Can magnesium pressure die casting be used for complex designs?
Yes, magnesium pressure die casting allows for the precise creation of complicated, lightweight parts with thin walls and detailed designs.
What are common applications of the magnesium die casting process?
Common applications of the magnesium die casting process include automotive parts, electronic housings, aerospace components, and handheld device frames.
How does magnesium die casting benefit automotive parts manufacturing?
Magnesium die casting offers lightweight, high-strength parts, enhancing fuel efficiency, vehicle performance, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
What are the benefits of high precision magnesium alloy die casting?
High precision magnesium alloy die casting provides lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant parts with exceptional detail, enhancing performance and reliability in demanding applications.
