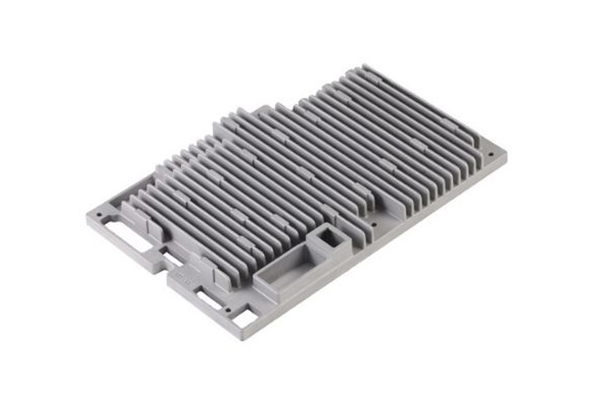
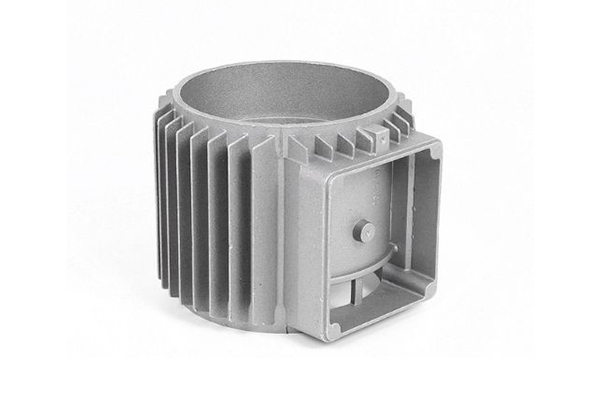
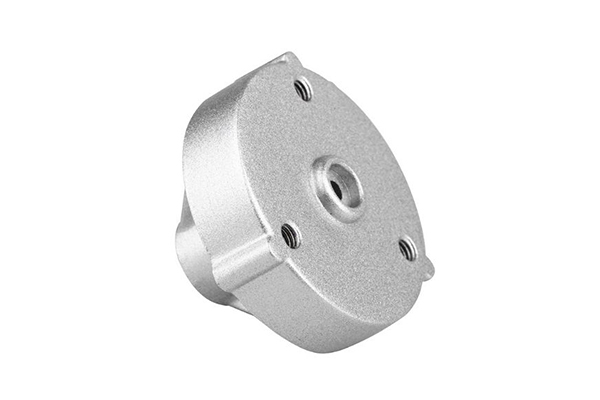
Custom Aluminum Die Casting Manufacturer
- Our aluminum die casting service provides lightweight, corrosion-resistant, precision parts, ensuring high quality and cost-effectiveness for diverse applications.
- We offer tailored solutions to meet specific customer requirements, ensuring that every part is designed and manufactured to exact specifications.
- Excellent Dimensional Accuracy (±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm)
- Aluminum Alloy Material Diversity
- Various Surface Treatments
- Cost Efficiency For Large Parts
- Application Versatility
Aluminum Die Casting Process
Raw Material Confirmation
Ensure the quality and suitability of aluminum alloys for the die casting process by thorough inspection and testing.
Mold Making
Create precise molds using advanced techniques to shape aluminum parts accurately, ensuring dimensional stability and consistency.
Rapid Prototyping
Produce initial prototypes quickly to validate design and functionality, allowing for adjustments before full-scale production.
Surface Treatment
Apply treatments such as polishing, painting, or anodizing to enhance the aesthetics, durability, and corrosion resistance of the final aluminum parts.
Aluminum Die Casting Methods

Aluminum High Pressure Die Casting
High pressure forces molten aluminum into a steel mold, producing precise, complex shapes. This method offers excellent dimensional accuracy, typically ranging from ±0.076 mm to ±0.178 mm, ideal for high-volume production of intricate aluminum components.

Aluminum Low Pressure Die Casting
Molten aluminum is gently pushed into the mold using low pressure. This process ensures high-quality aluminum parts with dimensional accuracy ranging from ±0.10 mm to ±0.25 mm, making it suitable for structural components requiring consistency.

Aluminum Gravity Die Casting
Utilizes gravity to fill molds with molten aluminum, producing strong, durable parts. Dimensional accuracy ranges from ±0.15 mm to ±0.25 mm, suitable for medium-volume production where mechanical strength and stability are critical.

Aluminum Vacuum Die Casting
This method employs a vacuum to draw molten aluminum into the mold, reducing gas porosity and improving part quality. Dimensional accuracy ranges from ±0.05 mm to ±0.13 mm, ideal for high-integrity components requiring precise tolerances.

Aluminum Squeeze Casting
Combines casting and forging, where molten aluminum is solidified under pressure within the mold. This process achieves high-density parts with dimensional accuracy from ±0.075 mm to ±0.125 mm, suitable for critical, high-strength applications.

Aluminum Semi-Solid Die Casting
Involves injecting semi-solid aluminum into a die, offering enhanced precision and reduced porosity. Dimensional accuracy typically ranges from ±0.04 mm to ±0.10 mm, making it ideal for complex shapes with stringent tolerance requirements.
Aluminum Alloys Model

A380
- Composition: Aluminum, Silicon (8.5%), Iron (0.9%), Copper (3.5%), Zinc (3%), Magnesium (0.1%).
- Melting Point: 566°C.
- Application: Automotive parts, consumer goods, engine brackets, rotors.

A356
- Composition: Aluminum, Silicon (7%), Magnesium (0.3%), Iron (0.2%), Copper (0.1%), Manganese (0.1%).
- Melting Point: 570°C.
- Application: Aerospace, automotive wheels, and structures.

ADC12 (A383)
- Composition: Aluminum, Silicon (10.5%), Copper (2%), Zinc (3%), Iron (0.9%), Magnesium (0.1%).
- Melting Point: 577°C.
- Application: Electronics housings, heat sinks, intricate components

A360
- Composition: Aluminum, Silicon (9%), Magnesium (0.5%), Copper (0.6%), Iron (0.6%), Zinc (0.5%).
- Melting Point: 566°C.
- Application: Engine components, high-performance automotive parts.

A390
- Composition: Aluminum, Silicon (17%), Copper (4.5%), Magnesium (0.5%), Zinc (0.5%), Iron (0.1%).
- Melting Point: 595°C.
- Application: Engine pistons, cylinder heads, high-wear components.

A413
- Composition: Aluminum, Silicon (12%), Magnesium (0.1%), Copper (0.1%), Iron (0.6%).
- Melting Point: 573°C.
- Application: Hydraulic components, cooling system parts.
Surface Treatment

Anodizing
Forms a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer on aluminum, enhancing surface hardness and allowing for color dyeing to improve aesthetics and durability.

Hard Anodizing
Similar to anodizing, it creates a thicker, harder oxide layer, providing superior wear and abrasion resistance for high-stress applications.

Painting
Involves applying liquid or powder coatings to aluminum surfaces, enhancing aesthetics and providing protection against corrosion with various color and finish options.

Chromate Conversion Coating
Creates a protective, corrosion-resistant layer on aluminum, improving paint adhesion and providing a conductive surface for electrical applications.

Electro-polishing
Smoothens and brightens aluminum surfaces by removing a thin layer of material, enhancing appearance and resistance to corrosion and wear.

Passivation
Removes surface contaminants and forms a protective oxide layer on aluminum, increasing corrosion resistance without significantly altering its appearance.

Powder Coating
Applies dry powder to aluminum, cures under heat, forming a durable, protective layer with corrosion resistance, enhancing aesthetics with various colors and finishes.

Sand Blasting
Propels abrasive materials at high velocity onto aluminum, removing contaminants and coatings. Cleans, prepares surface, enhances roughness and adhesion, creating a uniform matte finish.
Our Aluminum Die Casting Projects



