Cutting intricate designs in sheet metal presents a unique challenge that requires precision, expertise, and advanced tools. Whether creating parts for machinery, customized designs for architecture, or artistic pieces, the ability to cut detailed patterns into metal opens up a wealth of possibilities.
This article will guide you through the methods and tools commonly used for cutting intricate designs in sheet metal, along with some best practices for ensuring clean, accurate cuts.
Choosing the Right Sheet Metal for Intricate Cuts
The first step in cutting intricate designs is selecting the right type of sheet metal.
Common materials include:
- Aluminum: Lightweight and versatile, aluminum is easy to cut, making it ideal for intricate designs.
- Stainless Steel: Known for its strength and durability, stainless steel may require more powerful cutting tools, but it can handle intricate designs if the right methods are used.
- Brass and Copper: These materials offer an aesthetic finish and are relatively soft, making them easier to cut with the appropriate tools.
- Mild Steel: Suitable for larger, less delicate designs, mild steel can be used for intricate cuts with the right equipment.
Cutting Methods for Intricate Designs
Several sheet metal cutting techniques are available for sheet metal, each offering specific advantages for intricate designs.
1. Laser Cutting
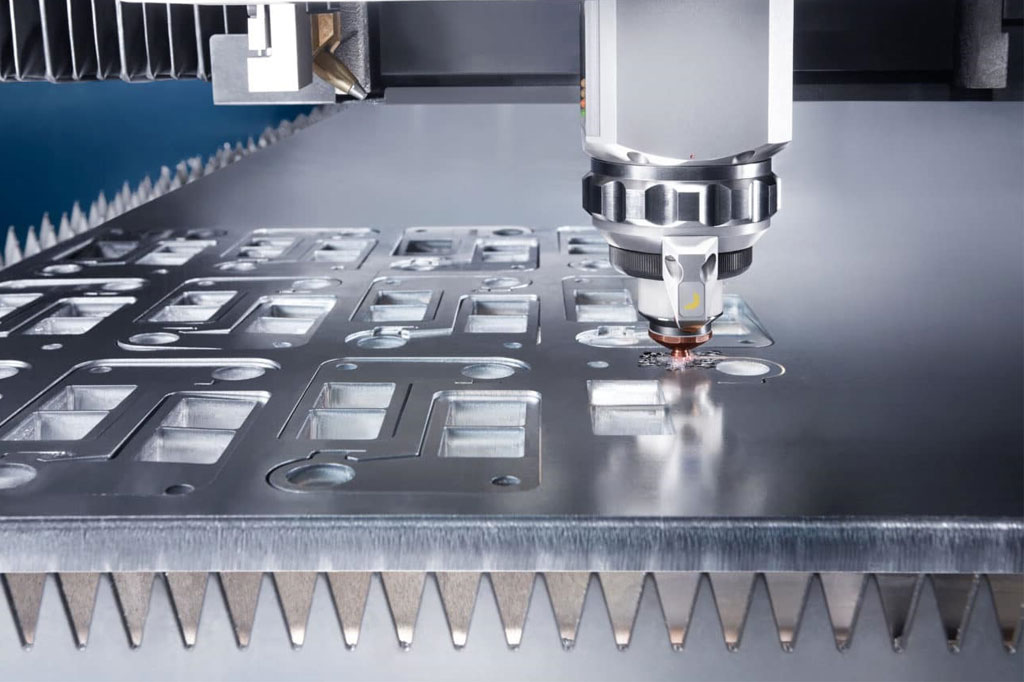

Laser cutting is a highly effective method for creating detailed designs, utilizing a powerful laser beam to melt or vaporize the metal.
The main advantages include:
- Precision: Laser cutting offers the finest level of precision, capable of cutting designs as small as 0.1mm in width.
- Complex Geometries: It can cut highly detailed shapes, curves, and tight corners.
- Clean Edges: Laser cutting results in smooth edges, minimizing the need for additional finishing.
Laser cutting works well on materials like aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel. However, laser cutting can be expensive and requires specialized equipment.
2. Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water combined with abrasive particles to gradually wear away the material. This method is ideal for intricate cuts because it offers:
- No Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): Unlike laser cutting, waterjet cutting doesn’t generate heat, so there is no risk of material distortion or thermal damage.
- Versatility: Waterjet cutting can work on almost any metal, including hard metals like titanium or high-strength steel.
Waterjet cutting is especially useful for thicker materials and for designs that may not suit laser cutting.
3. Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting uses ionized gas at high temperatures to cut through sheet metal. It’s faster than laser or waterjet cutting, but less precise. However, it can still be effective for cutting intricate designs when combined with fine settings.
Key advantages include:
- Speed: Plasma cutting is faster than other methods, making it cost-effective for larger production runs.
- Thickness Range: Plasma cutting is versatile and can efficiently handle a wide range of materials, from thin sheets to thicker plates.
While not as precise as laser cutting, plasma cutting is a good option when speed is a priority, and some post-processing may be done to refine the edges.
4. CNC Milling
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling is another precision method used for intricate designs. It involves a rotating tool that removes material from the sheet metal. While primarily used for three-dimensional parts, CNC milling can also be employed for intricate two-dimensional cuts.
The benefits include:
- Complex Geometries: CNC mills are capable of creating detailed 3D and 2D cuts with high accuracy.
- Versatility: CNC milling can cut through a wide range of metals, including tough, hardened steels.
This method is best for parts that require a high degree of precision, but the process can be slower and more expensive than laser or plasma cutting.
5. Die Cutting
Die cutting is a method often used for the mass production of sheet metal components with intricate shapes. A custom die is used to stamp out designs. While die cutting is ideal for repetitive parts, it’s less suitable for one-off projects or very fine details.
Best Practices for Cutting Intricate Designs

To achieve the best results when cutting intricate designs, keep these tips in mind:
1. Use the Right Tool for the Job
Choosing the appropriate cutting method is essential for intricate designs. For finer, delicate work, laser or waterjet cutting will likely offer the best precision. For larger projects or where speed is a factor, plasma cutting or CNC milling may be more suitable.
2. Optimize Design for Cutting
Ensure that your design is optimized for the chosen cutting method. For example, laser cutting works best with designs that avoid overly sharp internal corners, while waterjet cutting can handle more complex designs with tight angles.
3. Consider Material Thickness
The thickness of the material affects both the choice of cutting method and the complexity of the design. Thicker metals may require slower cutting speeds and more powerful equipment. For intricate designs, it’s generally better to work with thinner materials.
4. Test Your Design
It’s recommended to test your design on scrap material before cutting the final piece. This allows you to fine-tune settings such as cutting speed, power, and feed rate to ensure the final product meets your expectations.
5. Post-Cutting Finishing
After cutting intricate designs, finishing processes like deburring, sanding, or polishing may be required to smooth the edges and remove any sharpness or imperfections left from the cutting process.