Custom Die Casting Service
- Our die-casting service excels in high-volume production of precise components with complex geometries and tight tolerances.
- Utilizing advanced techniques, we achieve superior surface finishes directly from the mold, minimizing the need for additional machining solutions.
- Various Die Casting Process Types
- Tolerance: ±0.005" (0.127mm) ~ ±0.0015" (0.038mm)
- High Production Efficiency
- Complex Geometries
- Variable Wall Thicknesses
- Various Surface Treatments
- Reduction in Scrap
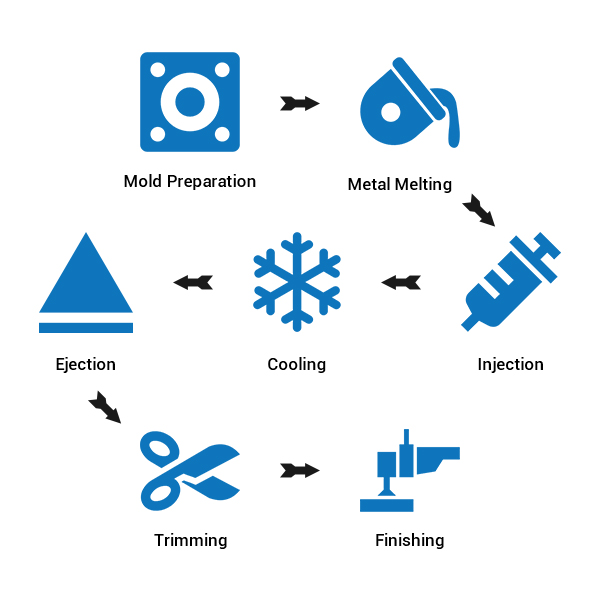
Common Steps of Die Casting
The die casting process creates complex metal components by injecting molten metal into precision molds,
producing high-quality parts with excellent accuracy.
producing high-quality parts with excellent accuracy.
Mold Preparation
Clean, lubricate, and securely clamp the die mold to withstand high-pressure injection.
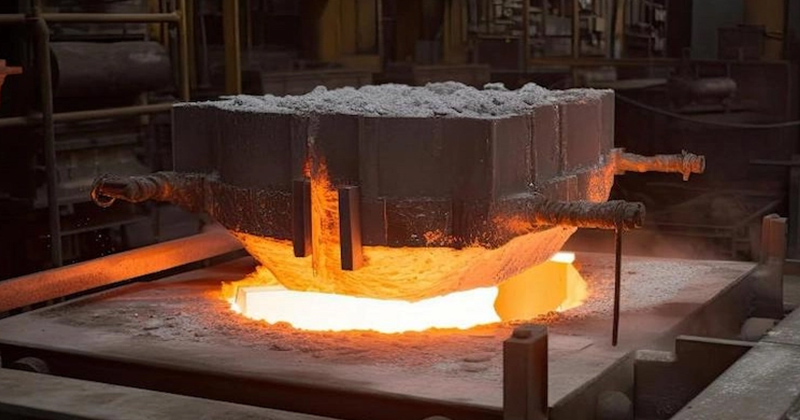
Metal Melting
Heat the chosen metal in a furnace until it liquefies.
Injection
Inject molten metal into the die cavity at high pressure to fill intricate details.
Cooling
Permit the molten metal to cool and solidify, molding itself to the shape of the die cavity.
Ejection
Open the mold and use ejector pins to release the solidified cast part.
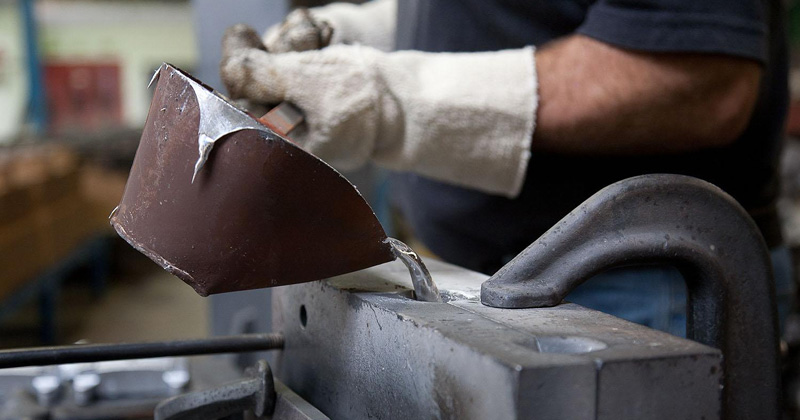
Trimming
Remove excess material (flash) from the cast part using manual or automated trimming processes.
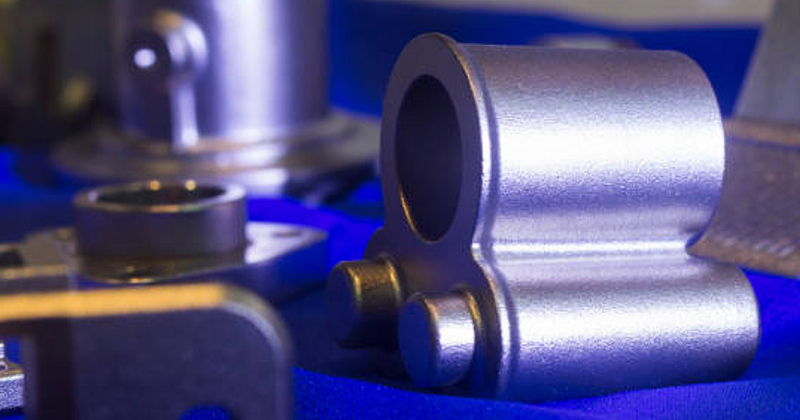
Finishing
Inspect the cast part for quality, dimensional accuracy, and perform any necessary finishing operations.
Die Casting Process Types
We explore the unique features, accuracies, and applications of six die casting processes, each with distinct characteristics
that make them suitable for different materials and requirements.
that make them suitable for different materials and requirements.

Hot Chamber Die Casting
- Integrated melting chamber: Rapid cycling and efficient metal injection.
- Injection pressures: 1,500 to 4,500 psi.
- Accuracy: ±0.005 inches (±0.127 mm).
- Scope: Ideal for low-melting-point metals like zinc and magnesium in automotive, electronics, and small mechanical parts.

Cold Chamber Die Casting
- Separate furnace for melting:Higher melting point metals.
- Injection pressures: 3,000 to 10,000 psi.
- Accuracy: ±0.005 inches (±0.127 mm).
- Scope: Ideal for metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze, used in automotive, aerospace, and large structural parts.

Gravity Die Casting (GDC)
- Natural Filling Process: Fills the mold cavity by using gravity.
- Injection Pressures: No external pressure; relies solely on gravity.
- Accuracy: ±0.010 to ±0.020 inches (±0.25 to ±0.50 mm).
- Scope: Ideal for medium to large-sized castings with simple geometries.
Vacuum Die Casting
- Air evacuation: Reduces gas porosity.
- Injection pressures: Vary by metal and design.
- Accuracy: ±0.001 to ±0.002 inches (±0.02 to ±0.05 mm).
- Scope: High-integrity automotive, aerospace, and electronics components.
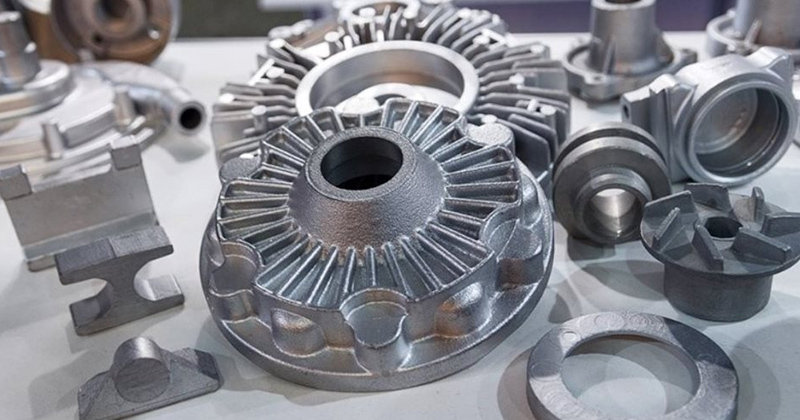

Squeeze Die Casting
- Combines die casting and forging: High-pressure solidification for dense parts.
- Injection pressures: Up to 10,000 psi.
- Accuracy: ±0.005 inches (±0.127 mm).
- Scope: Automotive suspension, aircraft parts, high-strength mechanical parts.
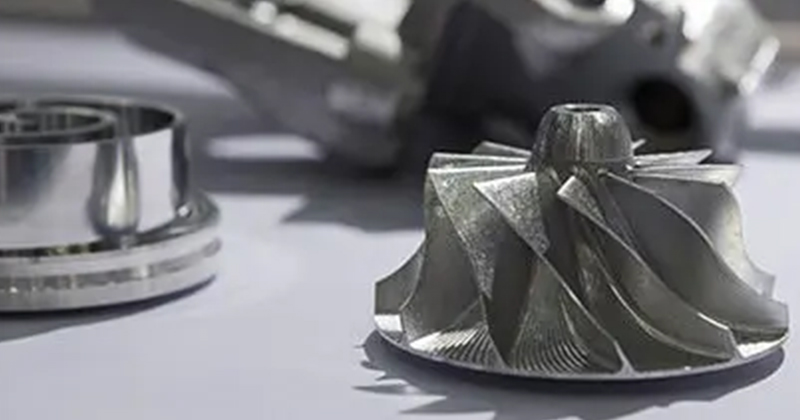

Semi-Solid Die Casting
- Uses semi-solid metal: Enhances accuracy, and reduces shrinkage.
- Injection pressures: 1,500 to 4,000 psi.
- Accuracy: ±0.0004 inches (±0.01 mm).
- Scope: Complex geometries in automotive, aerospace, high-precision parts.
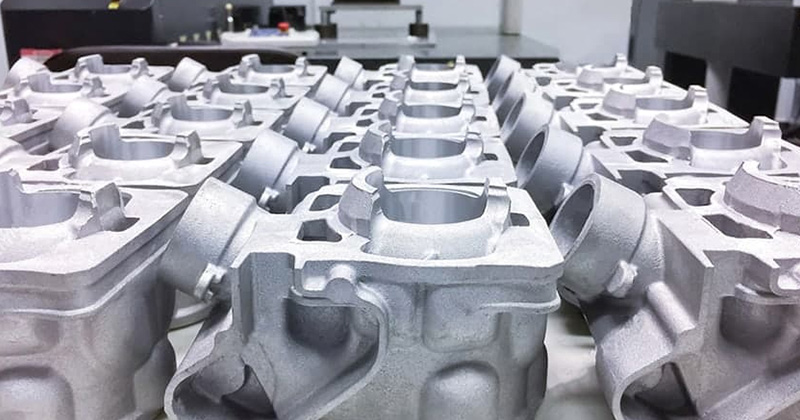

Low Pressure Die Casting
- Low pressure filling: 1-2 bar, reduces defects.
- Common materials: Aluminum, magnesium alloys.
- Accuracy: ±0.004 inches (±0.1 mm).
- Scope: Automotive wheels, structural components, large housing parts.
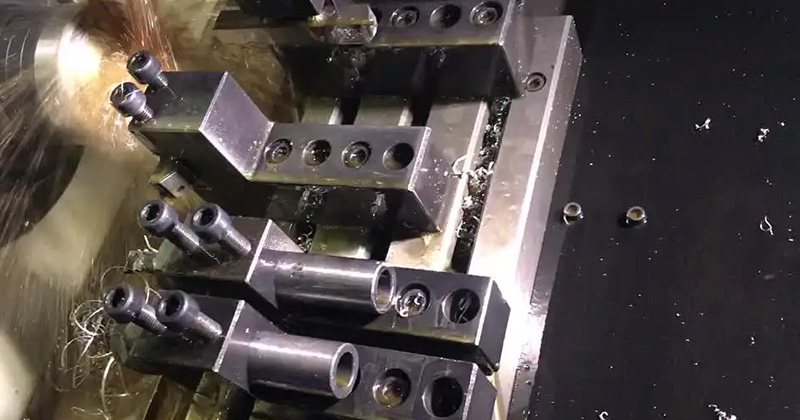

High Pressure Die Casting
- High-Pressure Injection: Molten metal is injected into a mold cavity at very high pressures.
- Injection pressures: 10,000 to 30,000 psi.
- Accuracy: ±0.002 inches (±0.05 mm).
- Scope: Ideal for high-volume production of complex and thin-walled parts.
Available Metal Materials
Explore the characteristics and applications of various die casting materials, including aluminum, zinc,
magnesium, copper, and other alloys across different industries.
magnesium, copper, and other alloys across different industries.

Aluminum Alloys
- Model: A380, A360, A356, A383, ADC12.
- Melting Point: 660.3°C.
- High Strength: Tensile strength typically 310 MPa (A380).
- Thermal Conductivity: 96-136 W/mK, ideal for heat dissipation.
- Applications: Corrosion resistance makes it suitable for automotive, aerospace, electronic, and structural parts.

Zinc Alloys
- Model: Zamak 3, Zamak 5, Zamak 7.
- Melting Point: 419.5°C.
- High Ductility: Elongation at break 10-15%, for complex shapes.
- Wear Resistance: Hardness around 82 Brinell (Zamak 3).
- Applications: Electrical conductivity of 27% IACS is ideal for electronics, hardware, automotive, and decorative parts.

Magnesium Alloys
- Model: AZ91D, AM60B, AS41B.
- Melting Point: 650°C.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Tensile strength 230 MPa (AZ91D).
- Good Machinability: Machining speeds 2.5x faster than aluminum.
- Applications: EMI shielding makes it suitable for automotive, aerospace, portable devices, and sporting goods.
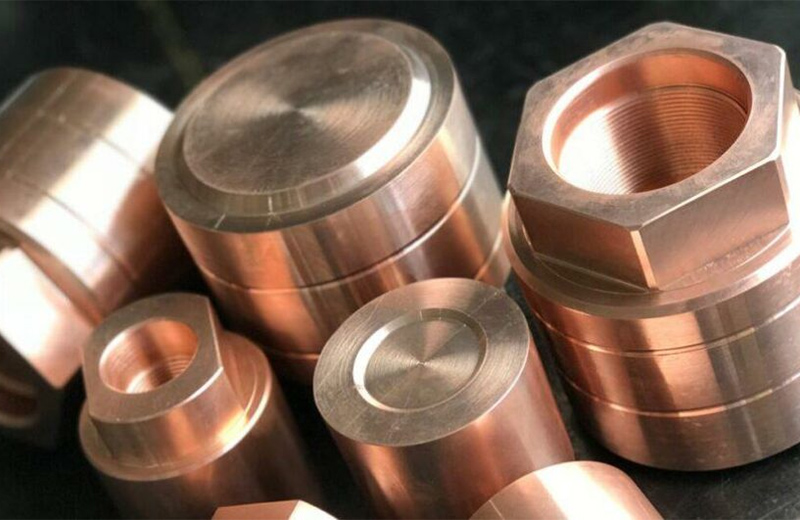

Copper Alloys
- Model: C84400, C84800.
- Melting Point: 1,085°C.
- High Strength: Tensile strength around 310 MPa (C84400).
- Corrosion Resistance: Excellent in various environments.
- Applications: High wear resistance is suitable for electrical, plumbing, industrial, and marine components.
Surface Treatment
Surface treatment in die casting involves various processes to enhance the properties and performance of cast metal parts.

Electroplating
- Purpose: Provides a decorative and protective layer.
- Benefits: Enhances corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and appearance.
- Materials Used: Chrome, nickel, zinc.

Anodizing
- Purpose: Creates a thick oxide layer on the surface.
- Benefits: Improves corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and dye retention for coloring.
- Materials Used: Mainly aluminum alloys.

Powder Coating
- Purpose: Provides a protective and decorative coating.
- Benefits: Provides a durable, uniform, and attractive finish with good corrosion resistance.
- Materials Used: Thermoplastic or thermoset polymer powder.

Painting
- Purpose: Adds a protective and aesthetic coating.
- Benefits: Enhances appearance, offers corrosion resistance, and allows for color customization.
- Materials Used: Acrylic, epoxy, polyurethane paints.
Passivation
- Purpose: Increases the corrosion resistance of metal surfaces.
- Benefits: Produces a shielding oxide layer and eliminates impurities.
- Materials Used: Nitric acid or citric acid solutions.

Sandblasting
- Purpose: Cleans and roughens the surface for better adhesion of coatings.
- Benefits: Enhances surface cleanliness and the adhesion of later coatings.
- Materials Used: Abrasive materials like sand, glass beads, aluminum oxide.

Polishing
- Purpose: Creates a smooth and shiny surface finish.
- Benefits: Enhances appearance and reduces surface roughness.
- Materials Used: Abrasive compounds and polishing wheels.

E-coating (Electrophoretic Painting)
- Purpose: Applies a thin, uniform protective coating.
- Benefits: Provides excellent corrosion resistance and uniform coating thickness.
- Materials Used: Electrically charged paint particles.

Chromate Conversion Coating
- Purpose: Provides corrosion resistance and a base for paint.
- Benefits: Enhances corrosion resistance and paint adhesion.
- Materials Used: Chromate compounds, suitable for aluminum and zinc alloys.
Our Die Casting Projects
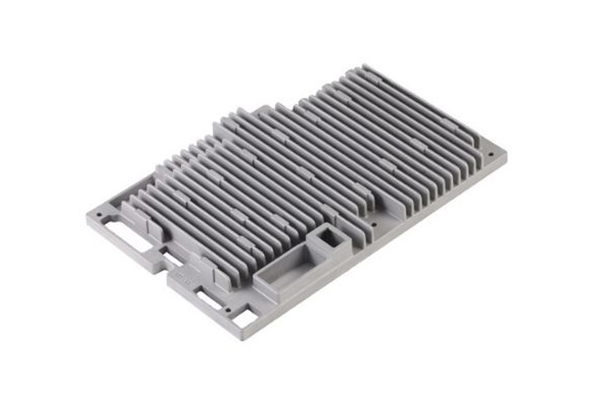
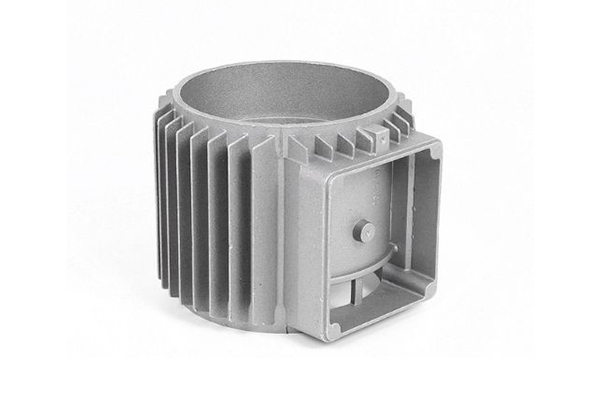
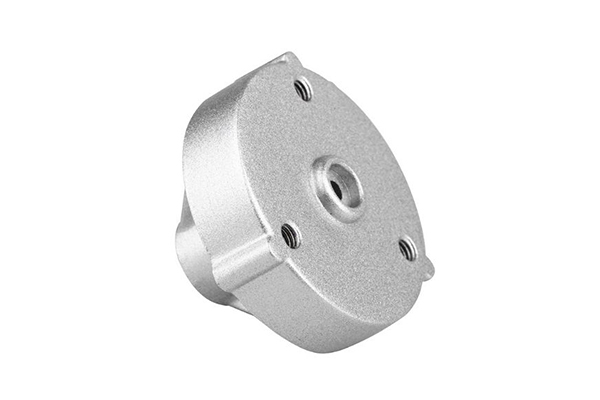



Die Casting Applications
Die casting is a versatile process used across industries to produce high-strength, lightweight, and precise components.

Automotive Industry
Die casting produces engine components, transmission parts, brackets, and housings, offering high strength, lightweight, and precise components essential for improving performance and fuel efficiency.

Aerospace Industry
In aerospace, die casting creates engine parts, structural components, and instrumentation housing with complex shapes to meet stringent performance and safety standards.

Industrial Machinery
Die casting is used in industrial machinery for pump components, valve bodies, and gearbox housings, ensuring high durability, precision, and cost-effectiveness.
Medical Devices
For medical devices, die casting manufactures diagnostic equipment housings and imaging equipment components, delivering the high precision, and intricate geometries required to meet medica’s strict standards.

Marine Industry
Die casting is used to produce corrosion-resistant boat engine components, structural parts, and fittings for marine vessels, ensuring robustness in harsh saltwater environments.

Sporting Goods
Die casting manufactures lightweight, strong bicycle components, fitness equipment parts, and durable outdoor gear, enhancing longevity in various sporting applications.
Popular Questions
What is the typical minimum wall thickness achievable in die casting?
The typical minimum wall thickness for die casting ranges from 0.020 to 0.080 inches (0.5 to 2.0 mm), depending on the material and specific die-casting process used.
How does zinc pressure die casting compare to aluminum and brass?
Zinc pressure die casting allows for thinner walls and finer details, with lower melting points and faster production cycles compared to aluminum and brass.
What are the Main Challenges of Hot and Cold Chamber Die Casting?
Hot chamber challenges include material limitations due to low melting points, while cold chamber challenges involve longer cycle times and more complex machinery.
How Does Aluminum Gravity Die Casting Compare to Pressure Die Casting?
Gravity die casting typically results in less porosity and better mechanical properties, though it may have slower production rates and be less suited for complex shapes compared to pressure die casting.
What are the Common Applications of High Precision Die Casting?
Common applications include engine components, medical device housings, electronic connectors, aerospace parts, and precision tools.
What Alloys are Typically Used in Stainless Steel Die Casting?
Common alloys include 304, 316, and 17-4 PH, selected for their specific mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
What quality standards are typically followed in CQS Precision Die Casting?
Quality standards such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (for automotive), and AS9100 (for aerospace) are often followed in CQS precision die casting to ensure the highest levels of quality and consistency.
How does Salt Core Die Casting work?
The process involves placing a pre-formed salt core inside the die casting mold. Next, the mold containing the salt core is filled with molten metal. After the metal solidifies, the salt core is dissolved using water or a suitable solvent, leaving the internal cavity or complex structure within the metal part.
