CNC boring is a machining technique used to widen or correct misalignments and inaccuracies in pre-drilled holes. The process is critical for achieving precise dimensions, fine surface finishes, and tight tolerances, especially when dealing with cylindrical holes in workpieces.
CNC boring automates this process, ensuring high precision, consistency, and efficiency.
Two main CNC boring types are vertical and horizontal CNC boring, each offering distinct advantages and suited to different tasks.
In this article, we will provide an in-depth comparison of these two types of CNC boring, analyzing their key differences, benefits, drawbacks, and applications. We will also explore which option is best for precision machining in various industries.
Vertical CNC Boring
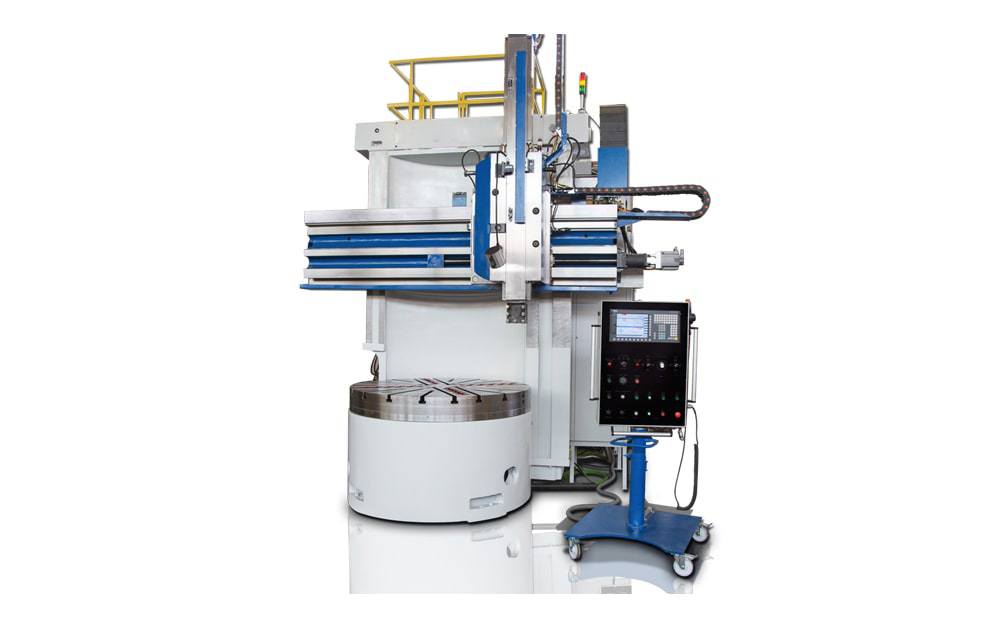

Vertical CNC boring machines, also known as vertical boring mills, have a vertically oriented spindle, and the workpiece is mounted on a rotating table. The cutting tool is positioned above the workpiece, moving downward to enlarge or refine the hole.
Advantages of Vertical CNC Boring
- Handling Large Workpieces: Vertical boring is well-suited for large, heavy workpieces with large diameters, such as those used in industries like aerospace, energy, and heavy machinery. The vertical setup leverages gravity to help keep the workpiece firmly positioned.
- Smaller Footprint: Despite handling large parts, vertical boring mills often require less floor space compared to their horizontal counterparts. They are therefore a great option for stores with little space.
- Ease of Loading and Unloading: The vertical orientation simplifies the loading and unloading process, as gravity helps position the workpiece on the table. This minimizes the physical effort required from operators and accelerates the production process.
- Stable Machining: The vertical setup provides added stability for large and heavy components, reducing vibration and ensuring better precision during the boring process.
Disadvantages of Vertical CNC Boring
- Limited for Long Parts: Vertical boring is less effective for machining long, slender parts like shafts and pipes. The vertical orientation does not provide adequate support for such parts, leading to potential deflection and inaccuracy.
- Chip Accumulation: Chips generated during the boring process tend to accumulate around the workpiece. This can obstruct the cutting tool, requiring frequent cleaning or chip removal systems to maintain productivity.
Horizontal CNC Boring
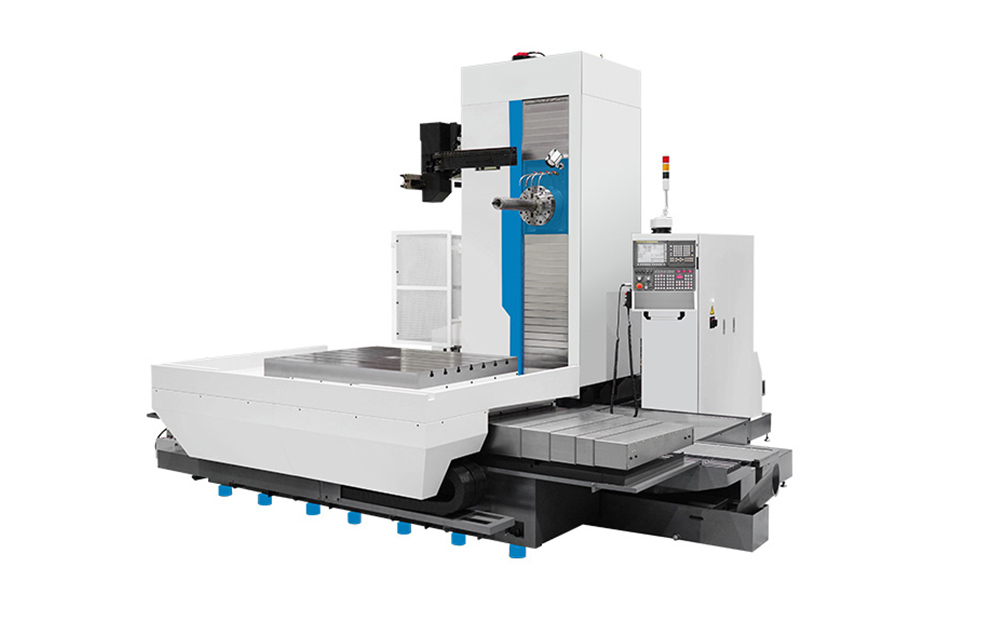

The spindle of a horizontal CNC boring machine is oriented horizontally. The workpiece is clamped and mounted on a stationary table, while the cutting tool moves horizontally to enlarge or finish the hole.
Advantages of Horizontal CNC Boring
- Versatility: Horizontal boring is highly versatile and capable of machining a wide variety of workpieces, from small to large, long, and complex shapes. They are ideal for parts that are longer than they are wide, such as pipes, axles, and shafts.
- Excellent Chip Evacuation: Gravity assists in chip removal in horizontal boring machines, ensuring that chips fall away from the workpiece during the cutting process. This helps maintain a cleaner workspace and allows for continuous, uninterrupted machining.
- Greater Flexibility: Horizontal boring offers more flexibility when it comes to multi-sided machining. It can work on different sides of a workpiece without requiring frequent repositioning, which improves efficiency in high-volume production environments.
- Increased Precision for Long Parts: Horizontal boring mills are particularly effective for long parts, as the horizontal orientation provides better support and minimizes deflection, resulting in more accurate machining.
Disadvantages of Horizontal CNC Boring
- Larger Footprint: Horizontal boring typically requires more floor space, making them less suitable for workshops with limited space.
- Challenging for Large-Diameter Parts: While horizontal boring is excellent for long parts, it is less effective for machining large-diameter workpieces, which are better handled by vertical boring mills.
Key Differences
While both vertical and horizontal CNC boring serve the same fundamental purpose, their differences in design, capabilities, and applications set them apart.
| Feature | Vertical CNC Boring | Horizontal CNC Boring |
| Spindle Orientation | Vertical | Horizontal |
| Best For | Large, heavy parts with large diameters | Long, slender parts; multi-sided machining |
| Chip Removal | Chips accumulate around the workpiece | Gravity assists in chip evacuation, maintaining cleanliness |
| Floor Space | Smaller footprint | Larger footprint, requires more space |
| Workpiece Handling | Easy loading/unloading due to gravity assistance | Requires more operator involvement for heavy parts |
| Workpiece Size | Ideal for large-diameter workpieces | Ideal for long, slender workpieces |
| Stability | Excellent stability for large parts | Increased precision for long parts |
| Flexibility | Less versatile, suited for specialized tasks | More flexible, ideal for multi-sided machining |
Productivity Consideration
Productivity in CNC boring depends on several factors, including part size, material, machining complexity, and production volume. Here’s how vertical and horizontal boring compare in terms of productivity:
Workpiece Size and Shape
Vertical CNC boring excels when working with large-diameter parts, such as those used in heavy equipment manufacturing, energy sector applications, and aerospace components.
Horizontal CNC boring is better suited for long, slender parts and workpieces that require machining on multiple sides.
Chip Management
Horizontal boring has the advantage when it comes to chip management. Gravity helps evacuate chips, keeping the workspace clean and reducing downtime.
Vertical boring may struggle with chip accumulation around the workpiece, requiring more frequent cleaning or advanced chip removal systems.
Flexibility
With its increased versatility, horizontal boring can perform more intricate and multi-sided machining tasks. Since multiple sides of a workpiece must be machined without repositioning, they are perfect for high-volume production operations.
Vertical boring is typically more specialized, and designed for repetitive, high-precision tasks involving large-diameter parts.
Space Considerations
Vertical boring machines require less floor space, making them a better choice for shops with space constraints.
Horizontal boring machines, due to their larger size and additional support systems, require more floor space, which may be a limiting factor for smaller workshops.
Applications

The choice between vertical and horizontal CNC boring services largely depends on the specific application and industry requirements.
Vertical CNC Boring Applications
- Heavy Equipment Manufacturing: Producing large-diameter components such as turbine housings, gearboxes, and flywheels.
- Energy Sector: Producing large components for power plants, wind turbines, and other energy infrastructure through precision machining.
- Aerospace: Manufacturing large, heavy components like engine casings and structural rings.
Horizontal CNC Boring Applications
- Automotive Industry: Producing long components such as drive shafts, engine blocks, and transmission parts.
- Aerospace: Machining structural supports, landing gear components, and other long, slender parts.
- General Machining: Horizontal boring is versatile enough to handle a wide range of cylindrical parts, including pipes, axles, and fittings.
Which is Best for Precision Machining?
The choice between vertical and horizontal CNC boring depends on the specific requirements of your business. Here are some factors to consider:
- If your business focuses on large-diameter parts, such as those used in the energy, aerospace, or heavy equipment industries, vertical CNC boring offers greater stability, precision, and ease of handling.
- If your business handles long, slender parts or requires multi-sided machining, horizontal CNC boring provides the flexibility and chip management necessary for high-precision, high-volume production.
- For businesses with limited floor space, vertical CNC boring machines are more practical due to their smaller footprint, while horizontal CNC boring machines require more space but offer greater versatility.